What is a Group & Assembly?
Both are collections of multiple Revit elements in one.
What is the difference?
1. Purpose of Use
Assembly is useful for producing detailed drawings or shop drawings enabling construction workflows. Basically, it is a part of the Revit project which gets built separately or wants to represent as a separate segment.
Whereas Group is useful when we have repetitive elements or layout.
2. Elements
Assembly cannot be created containing rooms, annotation, and detail items.
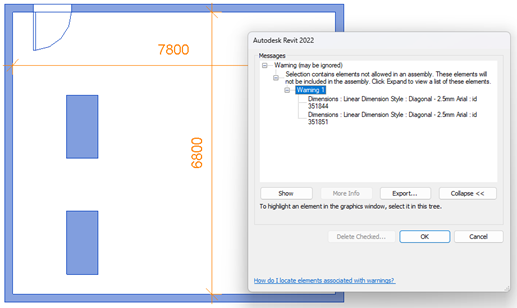
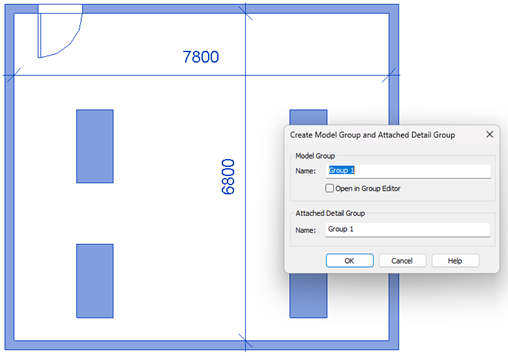
Whereas Group can be created containing rooms, annotation & detail items. (Model Group, Detail Group)
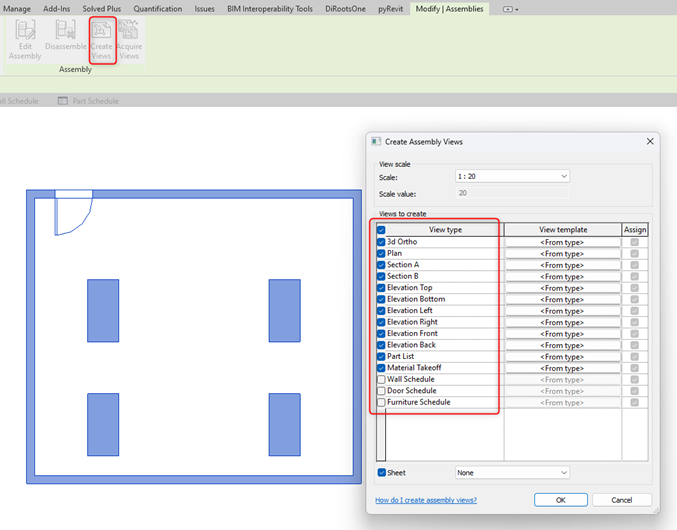
3. Separate Set of Views
Assembly provides a function to create a different set of views (Floor Plans / Ceiling Plans/ Elevation/ Section/ 3D Views/ Schedule) just containing that assembly.
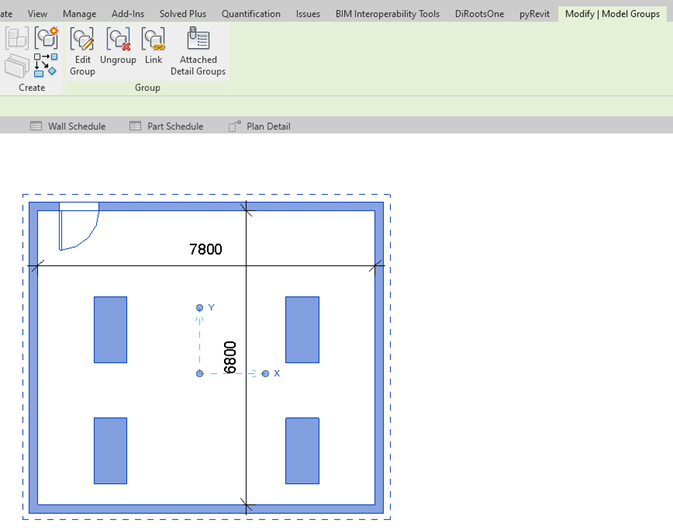
Whereas Group does not have a such function of creating a separate set of views just for the group.
4. Editing Capabilities
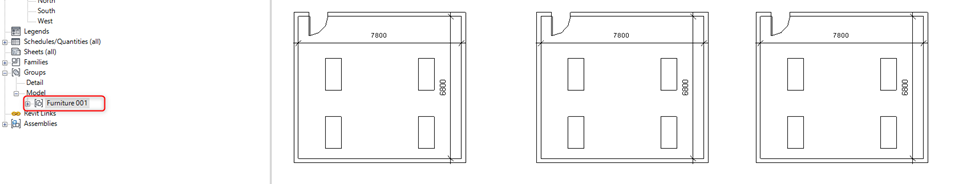
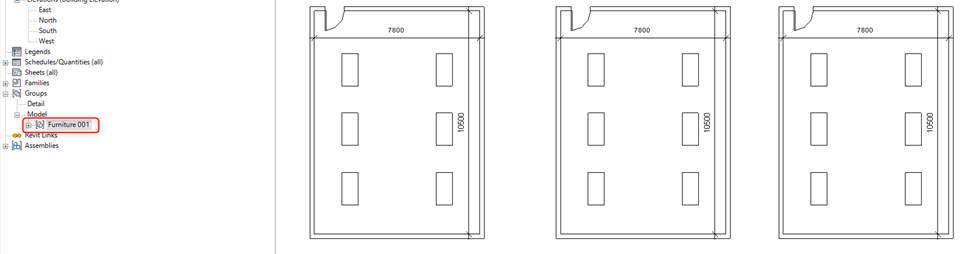
Assembly when edited creates a separate assembly it doesn’t make changes in similar assemblies in the project. This means when the assembly is created design must be completed.
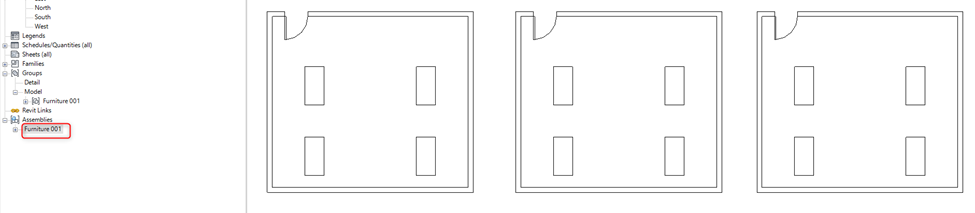
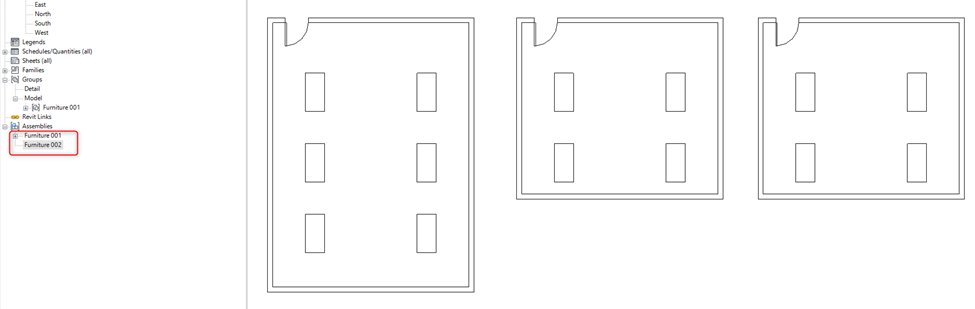
Whereas when edits are made inside a group do not create a separate group instead it updates all the similar groups in the project.
5. Exclusion of Elements
Assembly does not have a separate function of exclusion, unlike Groups.
Whereas in a Group when a single element of a group is excluded it doesn’t make changes in similar groups. It also has the option of restoring all excluded elements in a group. It provides more flexibility in terms of making changes in a group
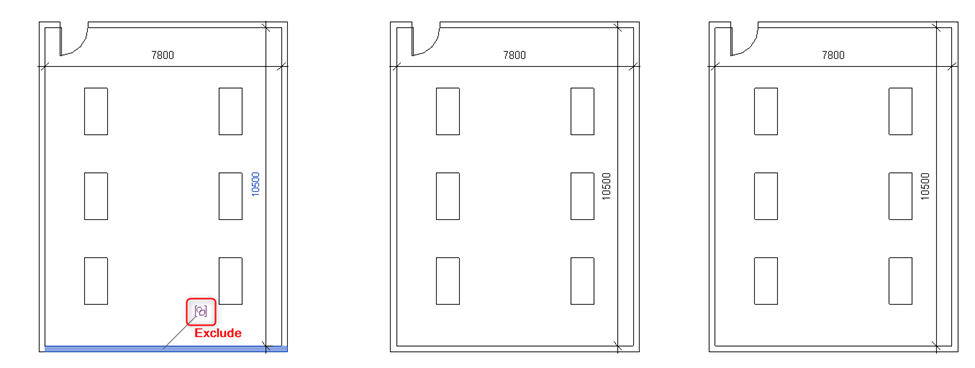
6. Deletion
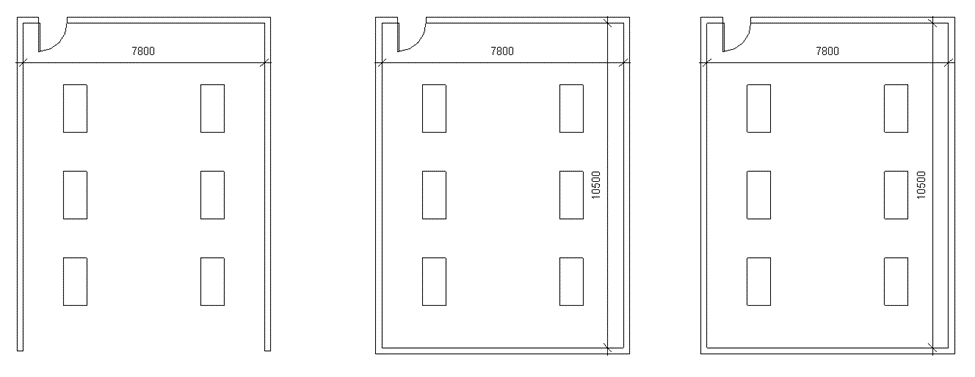
When a particular assembly is deleted in a view it completely gets deleted from the project.
Whereas when a Group is deleted in a view it remains in the project and can be used later to place back in the project.
7. Separate Revit Link
Assembly cannot be created as a separate link.
Whereas Group can be converted into a separate Revit Project and linked into the current file as a Revit Link.
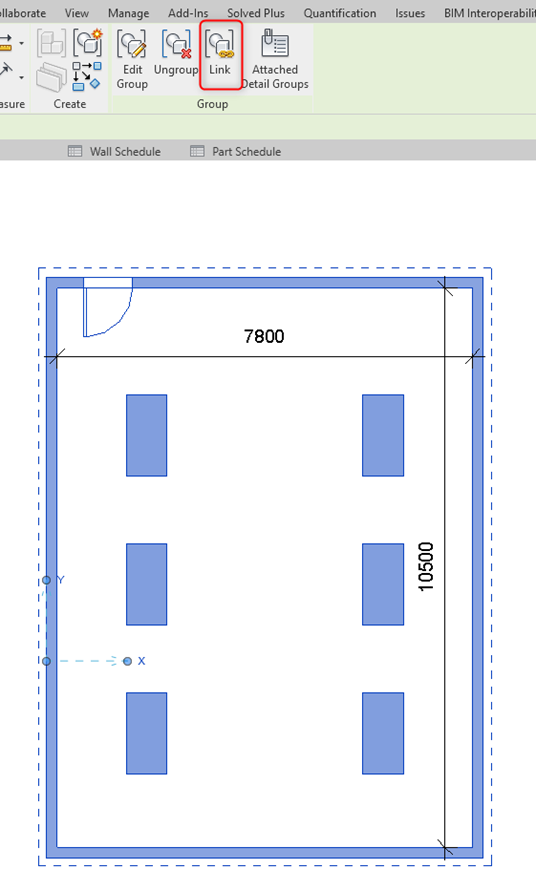
Summary
| Can include multiple Elements | Separate Views | Flexibility to Edit | Can include Rooms | Can include Annotation/Detail Item | Can include Design Option | Exclude certain element | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GROUP | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| ASSEMBLY | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | No | No |